An STT-MRAM based reconfigurable computing-in-memory architecture for general purpose computing
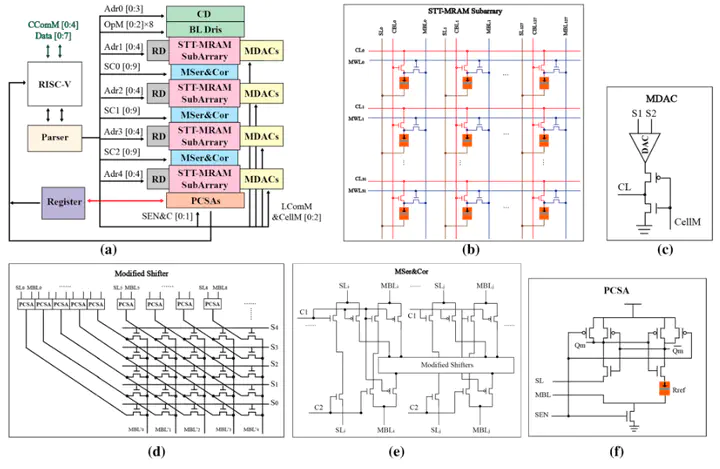 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
Recently, many researches have proposed computing-in-memory architectures trying to solve von Neumann bottleneck issue. Most of the proposed architectures can only perform some application-specific logic functions. However, the scheme that supports general purpose computing is more meaningful for the complete realization of in-memory computing. A reconfigurable computing-in-memory architecture for general purpose computing based on STT-MRAM (GCIM) is proposed in this paper. The proposed GCIM could significantly reduce the energy consumption of data transformation and effectively process both fix-point calculation and float-point calculation in parallel. In our design, the STT-MRAM array is divided into four subarrays in order to achieve the reconfigurability. With a specified array connector, the four subarrays can work independently at the same time or work together as a whole array. The proposed architecture is evaluated using Cadence Virtuoso. The simulation results show that the proposed architecture consumes less energy when performing fix-point or float-point operations.